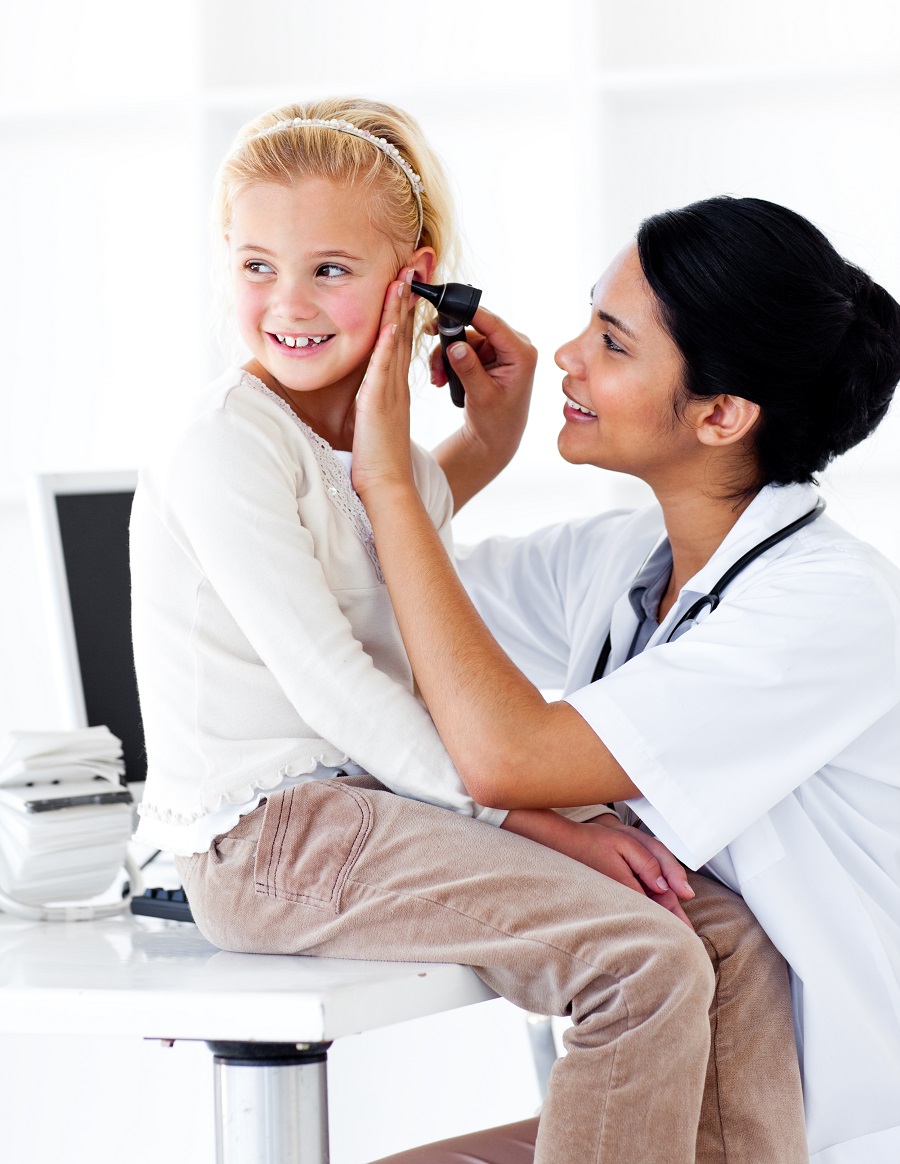
Discussing Otitis Externa in Children with Parents
Otitis externa (swimmers’ ear) is an infection of the ear canal. It is caused by different types of germs, bacteria or fungi getting into the ear canal and is very common in children who swim and play a lot in the water, hence the name swimmers’ ear.
The condition is more prevalent during the summer when swimming, pool sports and activities are more common. Moisture buildup in the ear canal can irritate the skin allowing germs to get a hold and cause an infection.
Swimmers’ ear can also develop without being in the water. An infection can develop if the ear canal’s skin gets injured or a patient suffers from eczema or dry skin. Scratching the skin of the ear canal with cotton buds or from other foreign objects inserted into the ear canal can also increase the risk of otitis externa.
A patient with a middle ear infection can also develop otitis externa when the pus from the infection drains into the ear canal through a perforation in the eardrum.
The signs and symptoms of otitis externa can include:
-
- Ear pain that intensifies when the out ear is pulled or pressed
- Pain experienced while chewing food or gum
- Itchiness in the ear canal before pain develops
- Redness or swelling of the outer ear
- Swollen and tender lymph nodes around the ear
- Discharge from the ear canal
- Dulled hearing
Preventative advice to give to parents
Parents concerned about swimmers’ ear can be advised to treat their child’s ears with drops containing a dilute solution of acetic acid or alcohol, which can be purchased over the counter from a pharmacy. The drops can be applied after swimming to prevent otitis externa but shouldn’t be given to children with ear tubes or a hole in the eardrum.
Parents should be advised not to clean their children’s ears with cotton buds or insert anything into the ear canal. They can gently dry their children’s ears after swimming with a hairdryer on a cool setting.
Parents should also be advised to seek medical help should their child develop an ear infection. They may have a severe condition that must be treated with oral medication to clear up. In more serious cases, it may be necessary to take a swab of the ear discharge and test to identify which fungi or bacteria are causing the infection for more targeted treatment.
Should a child develop otitis externa, parents should be advised to avoid swimming and do their best to keep water out of their children’s ears while being treated for the infection. When showering or bathing, a cotton wool ball coated in petroleum jelly can be gently inserted into the ear to protect the ear canal from moisture.
Practitioner Development UK Limited offers a range of training courses and practical workshops for medical staff across all disciplines. We recommend the following online course for nurse practitioners and allied medical staff involved in assessing and treating minor paediatric illnesses.
P01 Paediatric minor illness: Online Accredited by the RCN Centre for Professional Accreditation
The RCN Centre has accredited this one-day online course for Professional Accreditation. It aims to boost the skills and confidence of Advanced Nurse Practitioners, Nurse Practitioners, School nurses, Practice Nurses, Health Visitors, and Allied Health Professionals who deal with minor childhood illnesses.
The programme focuses on providing health professionals that take paediatric medical histories and perform physical examinations and who want to extend their knowledge and skills by exploring more paediatric conditions in an evidence-based context.
The course will help health professionals with the following:
- Discuss and practice taking safe, developmentally appropriate histories for a variety of paediatric patient presentations
- Assess and identify various common paediatric minor illnesses.
- Identify and discuss appropriate additional diagnostics required for accurate patient assessment
- Discuss paediatric patient management, including referral requirements for safe practice
- Demonstrate your ability to integrate your diagnostic reasoning and patient management skills through case studies and review scenarios.